The Economics of Champagne: Market Trends, Global Shifts, and Investment Insights
Champagne’s allure extends far beyond the celebratory pop of a cork. As global demand for luxury goods rises, the sparkling wine market has experienced remarkable transformation, with Champagne standing at the intersection of tradition, prestige, and evolving consumer preferences. Recent years have witnessed a surge in interest from investors and collectors alike, driven by Champagne’s consistent performance, scarcity of vintage releases, and its symbolic role in Western-style celebrations and luxury experiences. Market trends reveal that Champagne is not only a beverage of choice for festivities but also a strategic asset in diversified investment portfolios, appealing to those seeking both tangible value and cultural cachet.
The global Champagne market is forecast to grow robustly, fueled by shifting demographics, increased affluence in emerging economies, and a heightened appetite for premium experiences. Producers are capitalizing on these shifts by expanding into new markets, while navigating challenges such as high production costs, regulatory complexities, and fluctuating international trade conditions. As the economics of Champagne evolve, understanding the interplay between supply, demand, and investment potential becomes crucial for stakeholders aiming to capture value in a market defined by both heritage and innovation.
Key Takeaways
- Global demand for champagne continues to rise, with the market projected to reach over USD 10 billion by 2030, driven by premiumization, emerging middle-class consumers, and evolving celebration trends in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East
- Champagne exports are becoming more selective and quality-focused as consumers shift toward organic, low-dosage, and small-lot offerings, especially in established markets like the US and UK
- Economic pressures and geopolitical tensions are reshaping the champagne trade, influencing everything from supply chain logistics to pricing strategies and market access in key regions
- Vintage champagne has emerged as a viable alternative investment, outperforming many traditional assets due to its scarcity, aging potential, and cross-border prestige among collectors
- Producers and investors are aligning with long-term trends, including sustainability, brand storytelling, and luxury experiences, as champagne maintains its position at the intersection of culture, finance, and celebration
Champagne Market Size and Growth Trajectory
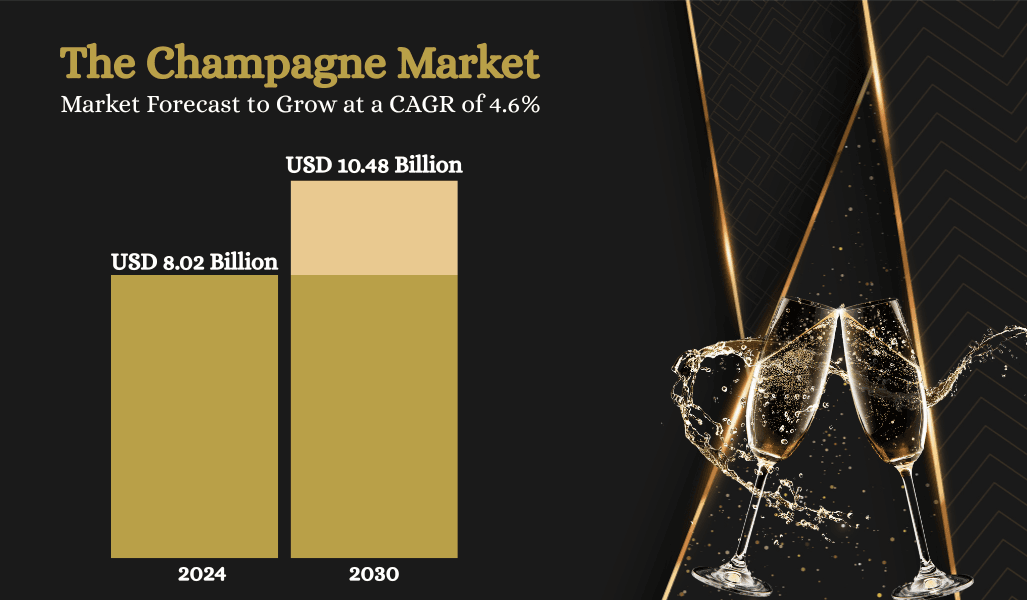
The global champagne market continues to experience healthy expansion despite economic fluctuations. Based on findings from Research and Markets, the sector reached a valuation of USD 8.02 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 10.48 billion by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.62% over the forecast period. This upward trend is largely driven by a rising appetite for premium beverages, especially in regions seeing increased discretionary spending.
While France, the United Kingdom, the United States, Japan, and Germany maintain their roles as top consumers of champagne, emerging markets are gaining ground. Countries like China, Brazil, and South Korea are contributing to global demand, particularly among younger consumers seeking aspirational luxury products. This shifting demand is encouraging producers to re-evaluate export strategies, packaging formats, and pricing tiers to match evolving expectations.
This upward momentum is attributed to several factors:
- Rising Affluence and Aspirational Consumption: Emerging markets, particularly in Asia and the Middle East, are witnessing increased demand for luxury beverages as symbols of status and celebration.
- Western-Style Celebrations: The adoption of Westernized social customs and luxury experiences in new regions further fuels Champagne’s global appeal.
- Brand Prestige and Heritage: Leading Champagne houses leverage their storied histories and brand equity to attract affluent consumers, reinforcing Champagne’s image as the pinnacle of sparkling wine.
However, the industry faces challenges that temper growth. High production costs, stemming from labor-intensive methods such as hand-harvesting and extended cellar aging, constrain margins—especially for smaller producers. Regulatory hurdles, including strict appellation controls and international trade barriers, add layers of complexity and cost, impacting both supply chains and market entry strategies.
Export Trends and Consumption Shifts
Recent figures confirm that global champagne exports are undergoing a notable adjustment. Data from the Comité Champagne reveals that in 2023, total worldwide shipments fell to 271.4 million bottles, representing a 9.2% decline from the previous year. This drop is linked to broader economic malaise, with inflation, geopolitical instability, and a cultural rethinking of celebration all contributing to more cautious consumer behavior.
According to interviews conducted by The Guardian with French producers, fewer consumers are reaching for champagne to mark life events, weddings, or holidays. The social and economic turbulence of recent years has shifted focus toward simpler pleasures or more practical purchases. However, this doesn’t equate to a decline in interest across the board. In countries like Japan and South Korea, gifting champagne remains culturally significant, and growth continues in select urban centers across Asia and Africa.
In more established markets such as the UK and US, preferences are leaning toward quality over quantity. Shoppers are increasingly selective, looking for organic, biodynamic, and low-dosage options that reflect evolving health and sustainability values. As a result, champagne producers are adjusting their offerings, scaling back mass-market production, and focusing more intently on small-lot, expressive cuvées that cater to niche demand.
Global Shifts and Geopolitical Influences
The Champagne market is increasingly sensitive to global economic and geopolitical shifts. International trade dynamics, currency fluctuations, and supply chain disruptions can have pronounced effects on pricing and availability.
For example:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Trade disputes or changes in tariff regimes can disrupt exports, affecting Champagne’s reach in key markets.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Logistics challenges, such as those witnessed during global crises, highlight the need for robust contingency planning among producers and distributors.
- Consumer Demand Fluctuations: Economic volatility influences discretionary spending, making Champagne sales susceptible to broader market cycles.
Producers and investors must remain agile, tailoring strategies to the unique conditions of each market while anticipating regulatory and economic changes that could impact profitability and growth.
Price Stratification and Consumer Access
Champagne’s pricing structure has evolved, reflecting broader trends in income inequality and market segmentation. Research tracking Champagne prices in New York City from 1948 to 2013 revealed that while entry-level nonvintage bottles have become more accessible across income groups, flagship and vintage offerings have grown increasingly exclusive. The number of hours required to purchase high-end bottles has outpaced gains in disposable income, underscoring Champagne’s role as both a luxury and an investment vehicle.
This stratification is reinforced by the scarcity of vintage releases and the prestige associated with top producers. Limited production of exceptional vintages creates rarity, driving up prices and enhancing long-term value for collectors and investors5.
Champagne as an Investment: Returns, Risks, and Strategies

Champagne’s emergence as an investment asset is underpinned by its consistent outperformance within the fine wine sector. Over the past two years, investment-grade Champagne prices, as measured by indices like Liv-ex’s Champagne 50, have surged by more than 30%, outpacing other wine regions and many traditional asset classes.
Key Drivers of Investment Value
- Scarcity: Vintage Champagnes are produced only in years of exceptional grape quality, with top houses releasing limited quantities. This rarity underpins price appreciation, especially as bottles are consumed and supplies dwindle.
- Prestige and Global Demand: The enduring reputation of leading Champagne brands ensures steady demand, even during economic downturns. Brand recognition transcends borders, making Champagne a staple in luxury portfolios.
- Quality and Longevity: High-end Champagnes are renowned for their aging potential, with some vintages evolving and appreciating in value over decades. This longevity appeals to investors seeking assets with both cultural and financial returns.
| Asset Class | Historical Performance | Tangibility | Volatility | Liquidity |
| Champagne (Vintage) | High, steady growth | Yes | Moderate | Moderate |
| Government Bonds | Low, stable | No | Low | High |
| Commodities (Gold) | Moderate, cyclical | Yes | High | High |
| Equities | Variable | No | High | High |
Comparing Champagne to Other Assets
Champagne offers a unique blend of tangible value, moderate volatility, and the potential for significant long-term appreciation, especially when compared to traditional financial instruments.
Navigating the Investment Landscape
Expert guidance is essential for navigating the complexities of Champagne investment. Opportunities range from acquiring prestigious Grand Marque labels to exploring grower Champagnes, which offer diversification and unique market niches. Investors must consider:
- Provenance and Storage: Ensuring authenticity and optimal storage conditions is critical for preserving value.
- Market Timing: Entry points and holding periods can influence returns, with patience often rewarded as rare vintages appreciate over time.
- Risk Management: As with all investments, Champagne carries risks, including market fluctuations and potential loss of capital. Diversification and professional advice can mitigate these risks.
The Future Outlook for Champagne Economics

Looking ahead, the Champagne market is poised for continued growth and innovation. Producers are increasingly adopting forward-thinking strategies to address challenges related to supply, regulation, and shifting consumer preferences. The interplay between tradition and modernity will shape the industry’s trajectory, with sustainability, digital marketing, and experiential luxury emerging as key themes.
For investors and enthusiasts, the economics of Champagne present a compelling narrative—one where cultural heritage, market dynamics, and financial opportunity intersect. As global markets evolve, Champagne’s status as both a luxury good and a strategic investment asset is set to endure, offering value to those who appreciate its unique blend of history, scarcity, and prestige.
Sources:
Straits Research, “Champagne Market Size, Demand & Growth Report by 2033
Data Bridge Market Research, “Global Champagne Market – Industry Trends and Forecast to 2031
Cult Wines, “Investing in Champagne | Cult Wines“
Paul J. Merton, “Patterns of Relative Cost of Champagne by the Same Producer“
Wine Investment Magazine, “Investing in Champagne: What’s all the fizz about?“
Research and Markets, “Champagne Market Outlook Report: Industry Size, Competition, Trends and Growth Opportunities by Region, YoY Forecasts from 2024 to 2031”
Research and Markets. (2024). Champagne market: Global industry size, share, trends, opportunity, and forecast, 2020–2030F
https://www.theguardian.com/world/2025/jan/19/champagne-makers-sales-losing-fizz-global-gloom-changing-habits
